Properties of Graph Data Structure
In this page, we will learn about various properties of graph
Graph Properties
Adjacent Vertices(or) Neighbors
If there is an edge between two vertices, then these two vertices are said to be adjacent vetices. For example, from the graph below, A and B are adjacent vertices, but A and D are not.
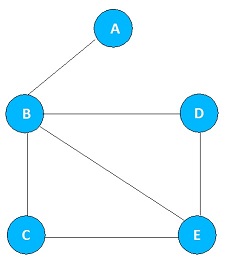
Path
Path is the sequence of vertices in which each vertex is adjacent to next one. In the above graph, A, B, C, E is one path and A, B, D, E is another path.
Cycle
Cycle is a path consisting of, at least 3 vertices that starts and ends with the same vertex.
Loop
Loop is a special case of cycle, in which a single arc begins and ends with same vertex.
Connected
If there is a path between two vertices, then we say that two vertices are connected







