C Arrays - declare Array, define Array, Array Example, 2d arrays
Multi Dimensional Arrays in C and C++ Programming
A multi-dimensional array is defined using multiple adjacent square brackets like a[4][3]. In a multi-dimensional array, there is no limit to specify the number of indices. For example, you can define an array with 5 indices like a[2][3][4][3][5] to store 2x3x4x3x5 = 360 number of elements. A two-dimensional or 2d array requires two indices, a three-dimensional array requires three indices, a four-dimensional array requires four indices, and so on.
Two-dimensional Array or 2d Arrays in C and C++ Programming
In C Programming, the two-dimensional array can be represented with two indices or two labels in square brackets. It can be declared as follows:
data-typename array-name[size][size];
It has (size*size) elements, which form imaginary grid in which every square is a variable or storage area.
The two-dimensional array can also be represented as rows and columns and it is also known as a matrix.
2d Array in C - Example
int Array[3][3];
The meaning of using two indices is that the first index refers to the number of rows in the grid whereas the second index refers to the number of columns in the grid.
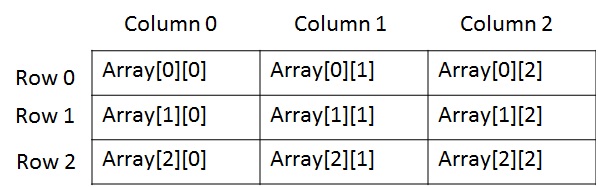
Two-dimensional or 2d Array Initialization
The elements of an array may be initialized with values enclosed in curly brace.
2d Array Example
int array[3][3]={{2,3,4},{9,4,7},{1,7,3}};
Here the braces are nested such that the inner braces enclose each row of the two-dimensional or 2d array. In memory, an array cannot be stored in grid instead it can be stored as one-dimensional array. Therefore arrays are stored in row-wise. The above array would be stored as
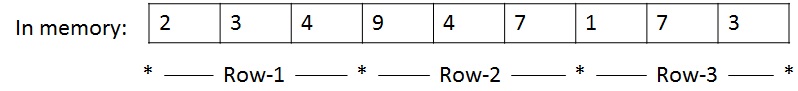
The multi-dimensional arrays may also be defined without a specific size as same as one-dimensional arrays. In the case of a two-dimensional array, only the left-most index ( the number of rows) is free, and the other dimensions must be given a definite value.
2d Array in C - Example 2
int array[][3]={
{2,3,4},
{9,4,7}
};
Usually, arrays of more than one dimension are simply handled by nested for loops. Therefore, a two-dimensional array may also be initialized as in the following example:
d Array in C - Example
main ()
{
int i,j;
float array[SIZE1][SIZE2];
for (i = 0; i < SIZE1; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < SIZE2; j++)
{
array[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
In case of 3-dimensional array, 3 nested loops would be needed.
Accessing of Arrays
To access an element of a two-dimensional array, the correct notation is to enclose each index in a separate pair of square brackets.
int result = array[1][2];
The above statement shows that 3rd element of the 2nd row of the array is assigned to the given variable.
strcat() - String Concatenation strcmp() - String Compare
strcpy() - String Copy strlen() - String Length








